A Multi-threaded/Multi-Process command-line utility and python package that downloads currency exchange rates from Histdata.com. Imports to InfluxDB. Can be used in Jupyter Notebooks.
Project description
histdata.com-tools
A Multi-threaded/Multi-Process command-line utility and python package that downloads currency exchange rates from Histdata.com. Imports to InfluxDB. Can be used in Jupyter Notebooks. Works on MacOS, Linux & Windows Systems. Requires Python3.10+
NEW: Expanded API support!!!
- histdata.com-tools
- Disclaimer
- Usage
- Setup
- Roadmap
Disclaimer
*I am in no way affiliated with histdata.com or its maintainers. Please use this application in a way that respects the hard work and resources of histdata.com
If you choose to use this tool, it is strongly suggested that you head over to http://www.histdata.com/download-by-ftp/ and sign up to help support their traffic costs.
If you find this tool helpful and would like to support future development, I'm in need of caffeine, feel free to buy me coffee!
Usage
Note #1 The number one rule when using this tool is to be MORE specific with your input to limit the size of your request.
Note #2 histdatacom is a very powerful tool and has the capability to fetch the entire repository housed on histdata.com. This is NEVER necessary. If you are using this tool to fetch data for your favorite trading application, do not download data in all available formats.
It is likely the default behavior will be modified from its current state to discourage unnecessarily large requests.
*please submit feature requests and bug reports using this repository's issue tracker.
Show the help and options
histdatacom -h
histdatacom -h
usage: histdatacom [-h] [-A] [-U] [--by BY] [--version] [-V] [-D] [-X] [-p PAIR [PAIR ...]] [-f FORMAT [FORMAT ...]] [-t TIMEFRAME [TIMEFRAME ...]] [-s START_YEARMONTH] [-e END_YEARMONTH] [-I] [-d] [-b BATCH_SIZE] [-c CPU_UTILIZATION]
[--data-directory DATA_DIRECTORY]
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Mode:
-V, --validate_urls Check generated list of URLs as valid download locations
-D, --download_data_archives
download specified pairs/formats/timeframe and create data files
-X, --extract_csvs histdata.com delivers zip files. Use the -X flag to extract them.
Config:
-p PAIR [PAIR ...], --pairs PAIR [PAIR ...]
space separated currency pairs. e.g. -p eurusd usdjpy ...
-f FORMAT [FORMAT ...], --formats FORMAT [FORMAT ...]
space separated formats. -f metatrader ascii ninjatrader metastock
-t TIMEFRAME [TIMEFRAME ...], --timeframes TIMEFRAME [TIMEFRAME ...]
space separated Timeframes. -t tick-data-quotes 1-minute-bar-quotes
-s START_YEARMONTH, --start_yearmonth START_YEARMONTH
set a start year and month for data. e.g. -s 2000-04 or -s 2015-00
-e END_YEARMONTH, --end_yearmonth END_YEARMONTH
set a start year and month for data. e.g. -e 2020-00 or -e 2022-04
Influxdb:
-I, --import_to_influxdb
import data to influxdb instance. Use influxdb.yaml to configure.
-d, --delete_after_influx
delete data files after upload to influxdb
-b BATCH_SIZE, --batch_size BATCH_SIZE
(integer) influxdb write_api batch size. defaults to 5000
System:
-c CPU_UTILIZATION, --cpu_utilization CPU_UTILIZATION
"low", "medium", "high". High uses all available CPUs OR integer percent 1-200
--data-directory DATA_DIRECTORY
Directory Used to save data. default is "./data/"
Info:
-A, --available_remote_data
list data retrievable from histdata.com
-U, --update_remote_data
update list of data retrievable from histdata.com
--by BY With -A, -U, to sort --by [pair_asc, pair_dsc, start_asc, start_dsc]
--version return current version of histdatacom.
Basic Use
Download and extract the current month's available EURUSD data for metatrader 4/5into the default data directory ./data
histdatacom -p eurusd -f metatrader -s now
include the -D flag to download but NOT extract to csv
histdatacom -D -p usdcad -f metastock -s now
Available Formats
The formats available are:
| metatrader |
| metastock |
| ninjatrader |
| excel |
| ascii |
histdata.com provides different resolutions of time depending on the format.
The following format/timeframe combinations are available:
| 1-minute-bar-quotes | all formats |
| tick-data-quotes | ascii |
| tick-last-quotes | ninjatrader |
| tick-bid-quotes | ninjatrader |
| tick-ask-quotes | ninjatrader |
CSV Dialect and Format Specifications
- For Detailed specifications for the CSVs that the histdata.com repo provides see histdata.com_data_specs.md
To download 1-minute-bar-quotes for both metastock and excel
histdatacom -p usdjpy -f metastock excel -s now
Date Ranges
date ranges are for year and month and can be specified in the following ways:
| [ -._] |
|---|
| 2022-04 |
| "2202 04" |
| 2202.04 |
| 2202_04 |
to fetch a single year's data, leave out the month
- note: unless you're fetching data for the current year, tick data types will fetch 12 files for each month of the year, 1-minute-bar-quotes will fetch a single OHLC file with the whole year's data.
histdatacom -p udxusd -f ascii -t tick-data-quotes -s 2011
to fetch a single month's data, include a month, but do not use the -e, --end_yearmonth flag
- if you're requesting 1-minute-bar-quotes for any year except the current year, you will receive the the whole year's data
- this example leaves out the
-p --pairflag, and will fetch data for all 66 available instruments
histdatacom -f metatrader -s 2012-07
Start & Now Keywords
you may have noticed that two special year-month keywords exist
start and now
startmay only be used with the-s --start_yearmonthflag and the-e --end_yearmonthflag must be specified to indicate a range of data
histdatacom -p audusd -f metatrader -s start -e 2008-12
nowused alone will return the current year-month- when used with as
-s nowit will return the most current month's data
histdatacom -p frxeur -f ninjatrader -s now
in the above example, no -t --timeframe flag was specified. This will return all time resolutions available for the specified format(s)
now when used with the -e --end_yearmonth flag is intended to be the end of a range. Rather, if the flags were to be -s 2019-04 -e now the request would return data from April 2019-04 to the present.
histdatacom -p xagusd -f ascii -1-minute-bar-quotes -s 2019-04 -e now
Multiple Datasets
multiple datasets can be requested in one command
this example with use the -e --end_yearmonth flag to request a range of data for multiple instruments.
- note: Large requests like these are to be avoided. remember to sign up with histdata.com to help them pay for network costs
histdatacom -p eurusd usdcad udxusd -f metatrader -s start -e 2017-04
CPU Utilization
One can set a cap on CPU Utilization with -c --cpu_utilization
- available levels are,
"low","medium","high" - OR
- integer percent 1-200
eg.
-c 100is equal to-c high
histdatacom -c medium -p udxusd -f metatrader -s 2015-04 -e 2016-04
Import to InfluxDB
To import data to an influxdb instance, use the -I --import_to_influxdb flag along with an influxdb.yaml file in the current working directory (where ever you are running the command from).
- ascii is the only format accepted for influxdb import.
- all histdata.com datetime data is in EST (Eastern Standard Time) with no adjustments for daylight savings.
- Influxdb does not adjust for timezone and all datetime data is recorded as UTC epoch timestamps (nano-seconds since midnight 00:00, January, 1st, 1970)
- this tool converts histdata.com ESTnoDST to UTC Epoch milli-second timestamps as part of the import-to-influx process
histdatacom -I -p eurusd -f ascii -t tick-data-quotes -s start -e now
influxdb.yaml
# a sample influxdb.yaml file.
influxdb:
org: influx_org
bucket: data_bucket
url: influx_server_api_url
token: influx_user_token
Download influxdb.yaml to your project's directory
curl "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dmidlo/histdata.com-tools/main/influxdb.sample.yaml" --output influxdb.yaml
API - Other Scripts, Modules, & Jupyter Support
histdatacom also has an API to allow developers and to integrate the package into their own projects. It can be used in one of two ways; The first being a simple interface to automate CLI interaction. The second is as an interface to work with the data directly in a notebook environment like Jupyter Notebooks.
CLI Automation
First import the required modules
import histdatacom
from histdatacom.options import Options
Create and Initialize a new options object to pass parameters to histdatacom
options = Options()
Configure for CLI automation
To automate the CLI, simply include one of the boolean behavior flags: options.validate_urls, options.download_data_archives, options.extract_csvs, and options.import_to_influxdb
- Each behavior flag implies the use of the preceding flags.
- histdatacom is an ETL pipeline (extract, transform, load) and each step depends on the preceding steps in the pipeline.
- For the
CLI, the order of operations are:- validate urls
- download zip files from histdata.com
- extract the csv from the zip archive
- transform the ESTnoDST datetime to UTC Epoch
ANDupload to InfluxDB.
# options.validate_urls = True
# options.download_data_archives = True # implies validate
options.extract_csvs = True # implies validate and download
# options.import_to_influxdb = True # implies validate, download, and extract
options.formats = {"ascii"}
options.timeframes = {"tick-data-quotes"}
options.pairs = {"eurusd"}
options.start_yearmonth = "2021-04"
options.end_yearmonth = "now"
options.cpu_utilization = 100
- when a behavior flag is included,
histdatacomassumes it is being used forCLIautomation exclusively and does not provide a return value.
at present, calling from another script or module is limited to using the __name__=="__main__" idiom.
if __name__=="__main__":
histdatacom(options)
Jupyter may be used normally
histdatacom(options) # (Jupyter)
Jupyter and External Scripts
As opposed to the CLI interface, one may wish to load data from histdata.com and work with it interactively (e.g. in a Jupyter notebook), or as part of a larger pipeline. To that end, histdatacom provides an option to specify a return type.
-
return types can be:
- A
datatableFrame - a
pandasdataframe - in Apache
arrowin-memory format
- A
-
to use
pandasorarrowformats you must install the required packagespip install pandaspip install pyarrow
-
All datetime is returned as milliseconds since January 1, 1970 (midnight UTC/GMT)
Import the required modules
import histdatacom
from histdatacom.options import Options
Initialize a new options object to pass parameters to histdatacom
options = Options()
Jupyter & External Script Options
options.api_return_type = "pandas" # "datatable", "pandas", or "arrow"
options.formats = {"ascii"} # Must be {"ascii"}
options.timeframes = {"tick-data-quotes"} # can be tick-data-quotes or 1-minute-bar-quotes
options.pairs = {"eurusd"}
options.start_yearmonth = "2021-04"
options.end_yearmonth = "now"
options.cpu_utilization = "high"
- This example uses just one pair/instrument/symbol
eurusdand just one timeframetick-data-quotes. When the api is called with this 'one-one` specificity, the api will directly return the requested data. - Regardless of the specified start_yearmonth and end_yearmonth, the resultant data will be sorted and merged into a single dataset.
Pass the options to histdatacom and assign the return to a variable
data = histdatacom(options) # (Jupyter)
print(data)
print(type(data))
datetime bid ask vol
0 1617253200478 1.17243 1.17244 0
1 1617253206261 1.17246 1.17248 0
2 1617253206362 1.17247 1.17249 0
3 1617253206946 1.17247 1.17250 0
4 1617253207121 1.17249 1.17250 0
... ... ... ... ...
18648493 1650664783081 1.07968 1.08042 0
18648494 1650664783182 1.07968 1.08039 0
18648495 1650664790108 1.07964 1.08032 0
18648496 1650664790958 1.07947 1.08032 0
18648497 1650664794462 1.07947 1.08032 0
[18648498 rows x 4 columns]
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
- When specifying more than one pair/symbol/instrument or timeframe, the api will return an list of dictionaries with references to the timeframe, pair, records used to create the data, and the merged data itself.
options.api_return_type = "pandas"
options.formats = {"ascii"}
options.timeframes = {"1-minute-bar-quotes"}
options.pairs = {"eurusd","usdcad"}
options.start_yearmonth = "2021-01"
options.end_yearmonth = "now"
options.cpu_utilization = "75"
data = histdatacom(options) # (Jupyter)
print(data)
print(type(data))
[
{
'timeframe': 'M1',
'pair': 'EURUSD',
'records': [<histdatacom.records.Record object ...>, ...],
'data':
datetime open high low close vol
0 1609711200000 1.22396 1.22396 1.22373 1.22395 0
1 1609711260000 1.22387 1.22420 1.22385 1.22395 0
2 1609711320000 1.22396 1.22398 1.22382 1.22382 0
3 1609711380000 1.22383 1.22396 1.22376 1.22378 0
4 1609711440000 1.22378 1.22385 1.22296 1.22347 0
... ... ... ... ... ... ...
484172 1650664440000 1.07976 1.08014 1.07976 1.08014 0
484173 1650664500000 1.08013 1.08021 1.07997 1.08000 0
484174 1650664560000 1.08000 1.08000 1.07956 1.07968 0
484175 1650664620000 1.07980 1.07980 1.07958 1.07968 0
484176 1650664680000 1.07980 1.07986 1.07963 1.07963 0
[484177 rows x 6 columns]
},
{
'timeframe': 'M1',
'pair': 'USDCAD',
'records': [<histdatacom.records.Record object ...>, ...],
'data':
datetime open high low close vol
0 1609711200000 1.27136 1.27201 1.27136 1.27201 0
1 1609711260000 1.27207 1.27241 1.27207 1.27220 0
2 1609711320000 1.27211 1.27219 1.27211 1.27219 0
3 1609711380000 1.27212 1.27261 1.27212 1.27261 0
4 1609711440000 1.27268 1.27268 1.27261 1.27261 0
... ... ... ... ... ... ...
483946 1650664440000 1.27121 1.27132 1.27114 1.27131 0
483947 1650664500000 1.27129 1.27137 1.27102 1.27106 0
483948 1650664560000 1.27107 1.27114 1.27098 1.27101 0
483949 1650664620000 1.27105 1.27105 1.27091 1.27091 0
483950 1650664680000 1.27091 1.27097 1.27073 1.27097 0
[483951 rows x 6 columns]
}
]
<class 'list'>
print(data[0]['timeframe'], data[0]['pair'])
print(data[0]['data'])
print(type(data[0]['data']))
M1 EURUSD
datetime open high low close vol
0 20210103 170000 1.22396 1.22396 1.22373 1.22395 0
1 20210103 170100 1.22387 1.22420 1.22385 1.22395 0
2 20210103 170200 1.22396 1.22398 1.22382 1.22382 0
3 20210103 170300 1.22383 1.22396 1.22376 1.22378 0
4 20210103 170400 1.22378 1.22385 1.22296 1.22347 0
... ... ... ... ... ... ...
484172 20220422 165400 1.07976 1.08014 1.07976 1.08014 0
484173 20220422 165500 1.08013 1.08021 1.07997 1.08000 0
484174 20220422 165600 1.08000 1.08000 1.07956 1.07968 0
484175 20220422 165700 1.07980 1.07980 1.07958 1.07968 0
484176 20220422 165800 1.07980 1.07986 1.07963 1.07963 0
[484177 rows x 6 columns]
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
at present, calling from another script or module is limited to using the __name__=="__main__" idiom.
if __name__=="__main__":
histdatacom(options)
Jupyter may be used normally
histdatacom(options) # (Jupyter)
Full Script Example
import histdatacom
from histdatacom.options import Options
from histdatacom.fx_enums import Pairs
def import_pair_to_influx(pair, start, end):
data_options = Options()
data_options.import_to_influxdb = True # implies validate, download, and extract
data_options.delete_after_influx = True
data_options.batch_size = "2000"
data_options.cpu_utilization = "high"
data_options.pairs = {f"{pair}"}# histdata_and_oanda_intersect_symbs
data_options.start_yearmonth = f"{start}"
data_options.end_yearmonth = f"{end}"
data_options.formats = {"ascii"} # Must be {"ascii"}
data_options.timeframes = {"tick-data-quotes"} # can be tick-data-quotes or 1-minute-bar-quotes
histdatacom(data_options)
def get_available_range_data(pairs):
range_options = Options()
range_options.pairs = pairs
range_options.available_remote_data = True
range_options.by = "start_dsc"
range_data = histdatacom(range_options) # (Jupyter)
return range_data
def print_one_datatable_frame(pair, start=None, end=None):
options = Options()
options.api_return_type = "datatable"
options.pairs = {f"{pair}"}
options.start_yearmonth = "201501"
options.formats = {"ascii"}
options.timeframes = {"tick-data-quotes"}
return histdatacom(options)
def main():
histdata_symbs = Pairs.list_keys()
# Oanda Symbols:
oanda_symbs = {"audcad","audchf","audhkd","audjpy","audsgd","audusd","cadhkd","cadjpy","cadsgd",
"chfhkd","chfjpy","euraud","eurcad","eurchf","eurgbp","eurhkd","eurjpy","eursgd","eurusd","gbpaud",
"gbpcad","gbpchf","gbphkd","gbpjpy","gbpsgd","gbpusd","hkdjpy","sgdchf","sgdhkd","sgdjpy","usdcad",
"usdchf","usdhkd","usdjpy","usdsgd","audnzd","cadchf","chfzar","eurczk","eurdkk","eurhuf","eurnok",
"eurnzd","eurpln","eursek","eurtry","eurzar","gbpnzd","gbppln","gbpzar","nzdcad","nzdchf","nzdhkd",
"nzdjpy","nzdsgd","nzdusd","tryjpy","usdcnh","usdczk","usddkk","usdhuf","usdmxn","usdnok","usdpln",
"usdsar","usdsek","usdthb","usdtry","usdzar","zarjpy"}
histdata_and_oanda_intersect_symbs = histdata_symbs & oanda_symbs
pairs_data = get_available_range_data(histdata_and_oanda_intersect_symbs)
for pair in pairs_data:
start = pairs_data[pair]['start']
end = pairs_data[pair]['end']
import_pair_to_influx(pair, start, end)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Setup
TLDR for all platforms
Install the latest version of datatable
- *this is a temporary fix until the datatable team updates PyPi. See this issue for more details
check out the section: Data Table Installation Options to either:
Install histdatacom
pip install histdatacom
to install latest development version
pip install git+https://github.com/dmidlo/histdata.com-tools.git
Vanilla MacOS and Linux
Create a new project directory and change to it
mkdir myproject && cd myproject && pwd
Create a Python Virtual Environment and activate it
python -m venv venv && source venv/bin/activate
Confirm Python Path and Version
which python && python --version
Build the latest version of datatable
follow the instructions from Install the latest version of datatable
Install the histdata.com-tools package from PyPi
pip install histdatacom
Run histdatacom to view help message and Options
histdatacom -h
Vanilla Windows Powershell
Launch a Powershell Terminal
- Run as Administrator (right-click on shortcut and click Run as Admin...)
Make sure python3.10 is in your system's executable path
python --version
- should be already set if you clicked the checkbox when installing python 3.10
- If not, you can run the following.
- you will need to relaunch powershell as admin.
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("Path", "$env:Path;C:\Program Files\Python310")
Change the Execution Policy to Unrestricted
Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -Force
Create a new directory and change to it
New-Item -Path ".\" -Name "myproject" -ItemType "directory"; Set-Location .\myproject\
Create a Virtual Environment and activate it
python -m venv venv; .\venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1
Confirm Path and Version
Get-Command python | select Source; python --version
Build the latest version of datatable
follow the instructions from Install the latest version of datatable
Install histdata.com-tools package from PyPi
pip install histdatacom
Run histdatacom to view help message
histdatacom -h
Anaconda Setup
Anaconda MacOS and Linux
Create a Project Directory and Change to it
mkdir myproject && cd myproject && pwd
Create a Python 3.10 Anaconda environment with conda and activate it
conda create -n py310 python=3.10 && conda activate py310
Check Python Path and Version
which python && python --version
Build the latest version of datatable
follow the instructions from Install the latest version of datatable
Install histdatacom package from PyPi
pip install histdatacom
Run histdatacom package to view help message
histdatacom -h
Anaconda Windows using the Anaconda Prompt
Create a Directory and Change to it
mkdir myproject && cd myproject && echo %cd%
Create a Python 3.10 Anaconda environment with conda and activate it
conda create -n py310 python=3.10 && conda activate py310
Check Python Path and Version
where python && python --version
Build the latest version of datatable
follow the instructions from Install the latest version of datatable
Install histdatacom package from PyPi
pip install histdatacom
Run histdatacom package to view help message
histdatacom -h
Datatable Installation Options
Install from Appveyor
Build wheels are pre-compiled versions of datatable, and would easily be the preferred route of installation while we wait for the datatable team to provide an official Python 3.10 package on PyPi. The only drawback is documenting the procedure as the wheel's URL expires monthly thus this documentation could go out of date rather quickly...
Activate Python Environment if you're using one
refer to the Create a Python Virtual Environment and activate it steps outlined for your platform
- Vanilla MacOS and Linux
- Vanilla Windows Powershell
- Anaconda MacOS and Linux
- Anaconda Windows using the Anaconda Prompt
Get the Build Wheel's URL for your platform
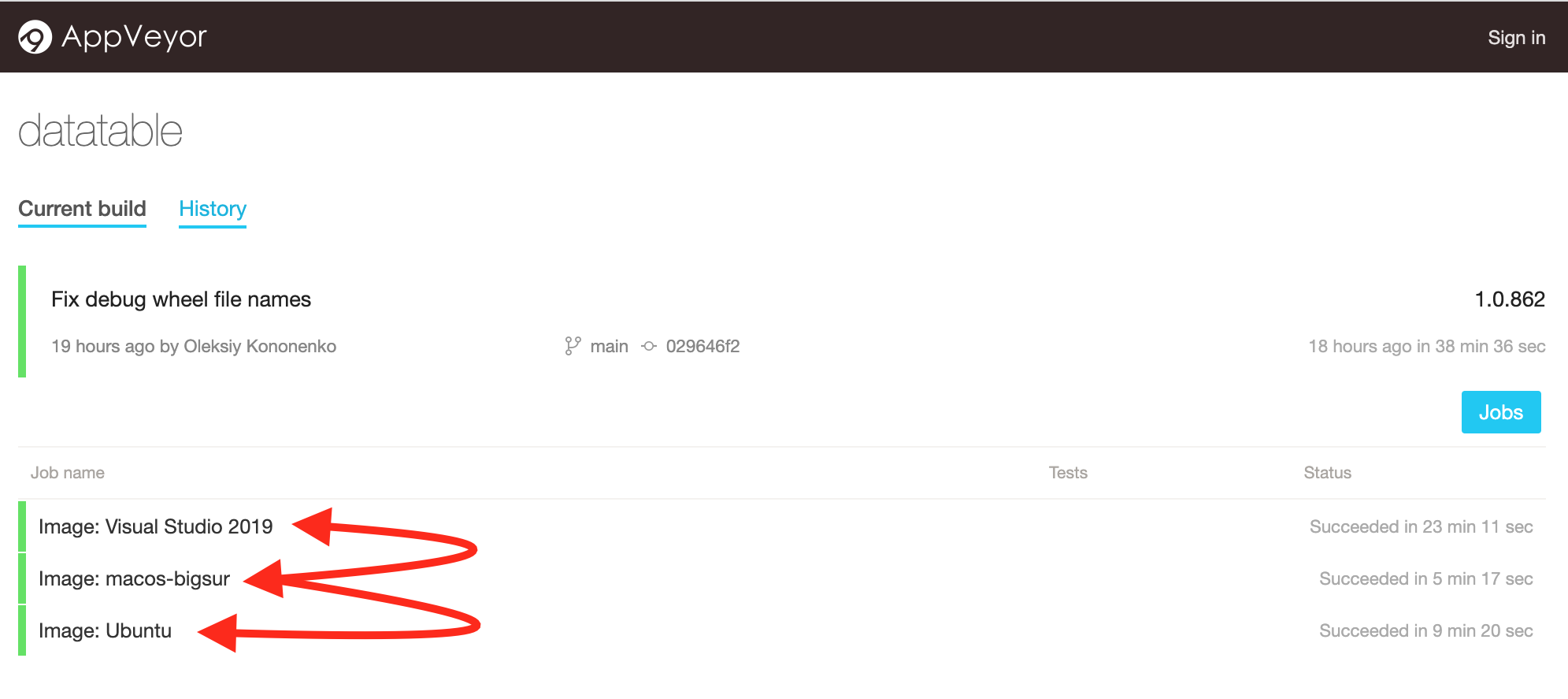
To find the latest build wheels for datatable, go to dataable's Appveyor CI/CD Instance:
- Select the Platform you're installing for:
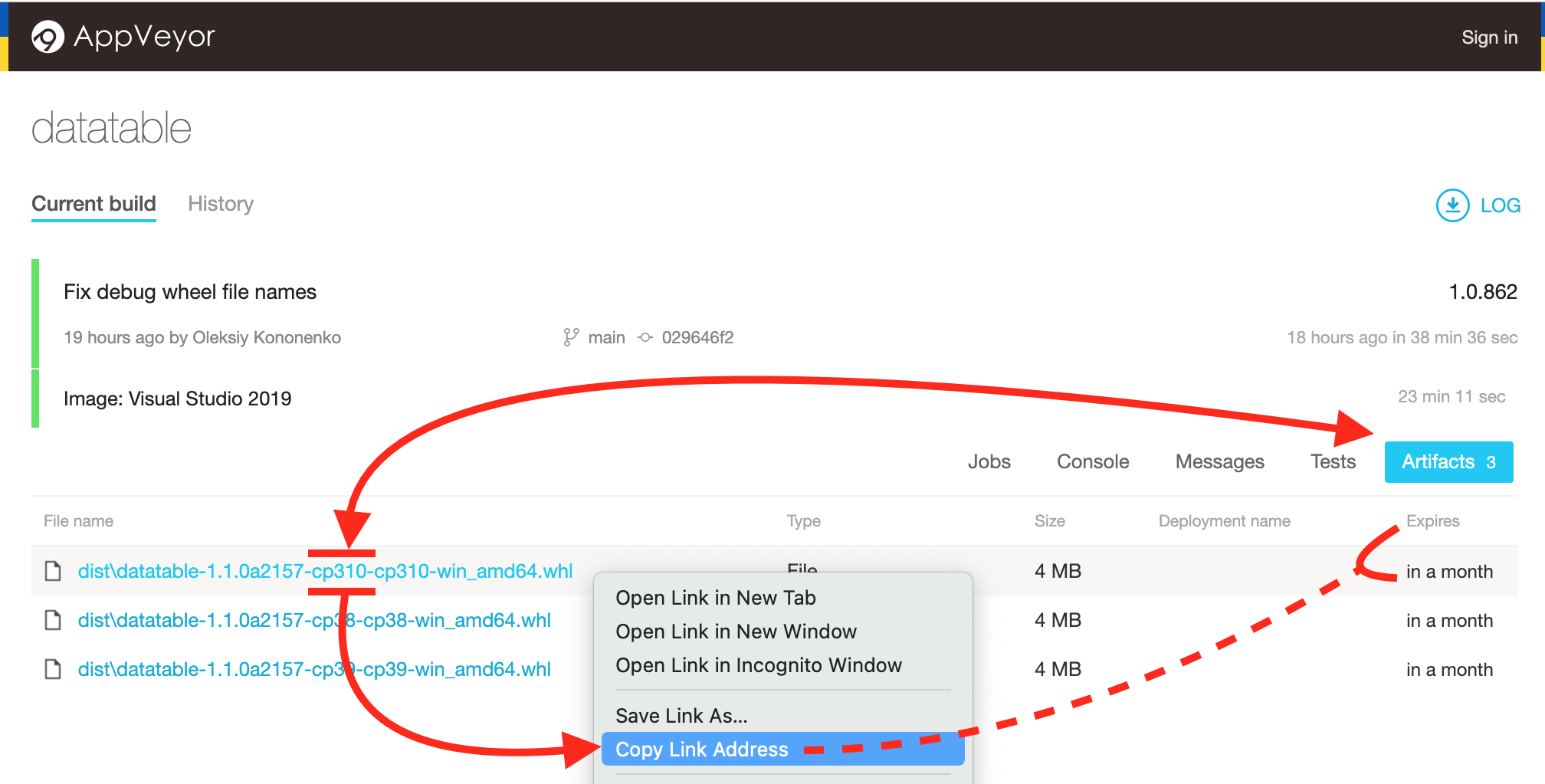
- Select
"Artifacts"and right/option-click on the filename that containscp310. e.g.dist\datatable-1.1.0a2157-cp310-cp310-win_amd64.whl - Select
"Copy Link Address"from your browser's context menu to copy the wheel's URL
Install datatable using pip with the wheel's URL from Appveyor
e.g. pip install {https://APPVEYOR DATATABLE BUILD WHEEL URL.whl}
Build from Source
- You will need a C++ compiler installed to build datatable from source
MacOS XCode Command Line Tools
- For MacOS, run
xcode-select --installfrom your terminal and confirm the prompts for download and installation of the xcode command-line tools.
Windows MSVC C++ Compiler
- For Windows, you need to download and install the Visual Studio Community Edition and choose the option
Desktop Development with C++, then select install.
Launch the Visual Studio command line environment (for Windows only)
- Open either a
powershell,cmd, orAnaconda Promptterminal- the setup scripts for the VS CLI environments are located in the
.\Common7\Tools\directory of your Visual Studio installation directory- e.g.
"C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Community\Common7\Tools\"
- e.g.
- the setup scripts for the VS CLI environments are located in the
- Run the VS CLI environment setup script
- for Powershell:
PS> "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Community\Common7\Tools\Launch-VsDevShell.ps1"
- for CMD and Anaconda Prompt:
> "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Community\Common7\Tools\LaunchDevCmd.bat"
- for Powershell:
Tell the datatable setup where to find the MSVC C++ compiler
- for Powershell:
PS> $env:DT_MSVC_PATH="$env:VSINSTALLDIR"+"VC\Tools\MSVC\"
- for CMD and Anaconda Prompt:
set DT_MSVC_PATH=%VSINSTALLDIR%VC\Tools\MSVC\
Return to Your Project's Directory
The Visual Studio command line environment setup scripts change your directory, you'll need to find your way back to your project's directory. I like to use the variable %USERPROFILE% to save myself some typing:
e.g. > cd %USERPROFILE%\Documents\projects\myproject
Activate Python Environment if you're using one
refer to the Create a Python Virtual Environment and activate it steps outlined for your platform
- Vanilla MacOS and Linux
- Vanilla Windows Powershell
- Anaconda MacOS and Linux
- Anaconda Windows using the Anaconda Prompt
Install datatable
pip install git+https://github.com/h2oai/datatable
Roadmap
Add Support for Anaconda- Implement MyPy static typing checking
- Implement UnitTesting with PyTest
- Create Binary Distributions
- See about packaging for different operating systems
- deb/rpm packaging
- NuGet/Chocolatey
- MacPorts/Homebrew
- See about packaging for different operating systems
- docker image
- Create Down-sampling to Standard Candlestick Timeframes
- Fix terminate on ctrl-c multiprocessing KeyboardInterupt
- Look at replacing beautifulsoup with html parser
- Refactor to make use of globals more readable
- add -v -vv and -vvv flags
- Change Record statuses to Enum
- Add -S —set-status flag
- Create a central place for exceptions
- Add the ability to import an order book to influxdb
- Add a --reset-cache flag to reset all or specified year-month range
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Hashes for histdatacom-0.78.4-py2.py3-none-any.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 63b175f75f840c12035edff476fa2d5c4dd6c858a3696c2c16829aa0bb6108cb |
|
| MD5 | e2e7fa972ef5cd322d06d1919aff1bcf |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 2a602e4b8cfafdd2584a730ba1f9b7f3042158d74766cb211fb1f3f48bc10a36 |