A Django app to provide elided pagination that is just... better
Project description
Better Elided Pagination
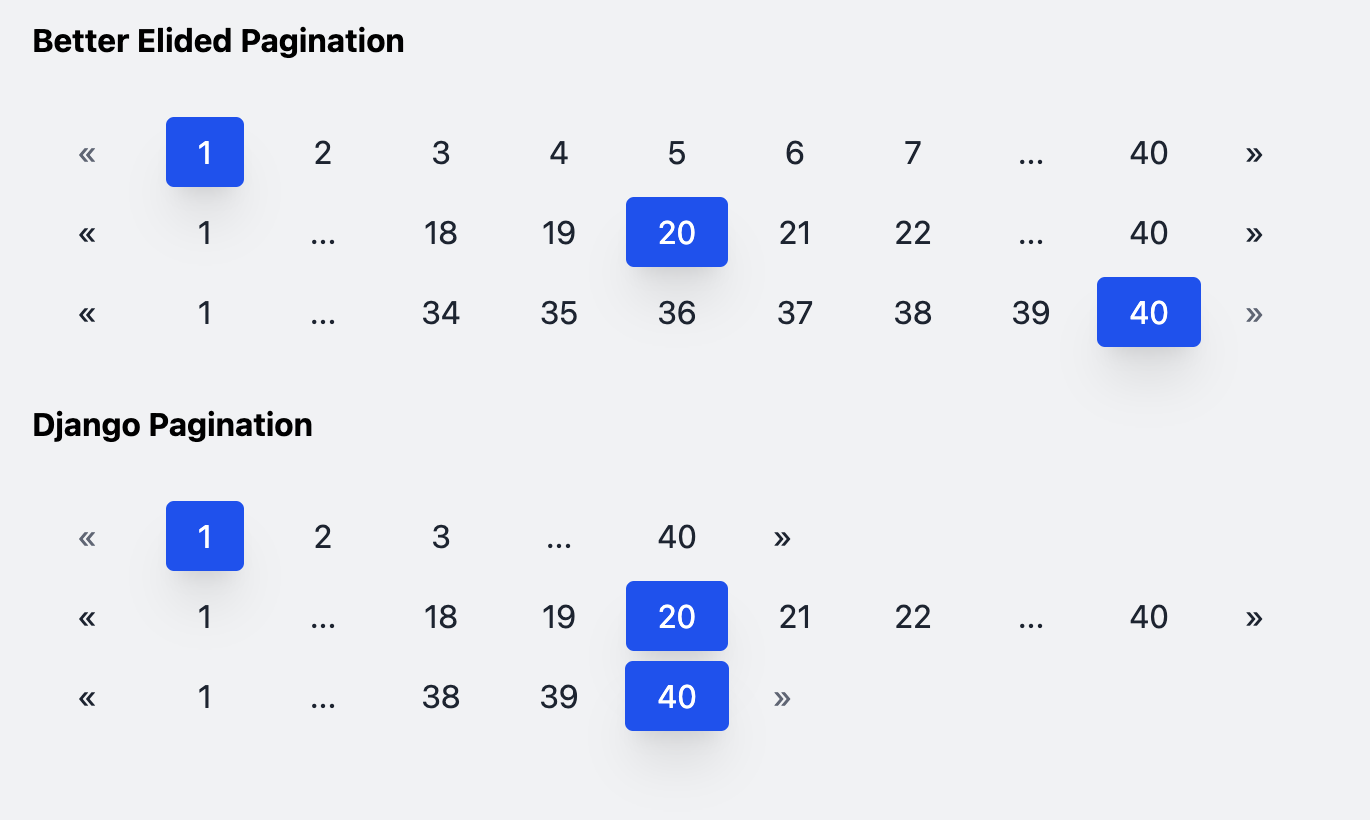
Better Elided Pagination extends the Django Pagination class to provide elided pagination (pagination with ellipses) that does not change lengths when the selected page is near the start or end of the list. The list of pagination nodes will have a predictable and fixed length when the number of nodes exceeds the desired length of the node list.
The following illustrates the difference between Django's built in elided pagination and this project's "better" elided pagination:
Compatible with Django 3.0+
Compatible with Tailwind 1.9.6+ if using Tailwind CSS
Installation
PIP
This will install the latest stable release from PyPi.
pip install django-better-elided-pagination
Usage
The complete example in the next section assumes you are using Tailwind CSS in your project. The html_list property will generate a list of HTML nodes styled using Tailwind CSS classes. If you prefer to style the pagination nodes yourself, you may simply use:
from better_elided_pagination.paginators import BetterElidedPaginator
def some_view(request):
items = [str(x) for x in range(1, 41)] # the items to be paginated - can be a list or queryset
pagination = BetterElidedPaginator(
request,
items,
3, # items per page
)
elided_list = pagination.get_elided_page_range()
.get_elided_page_range() will return a generator fuction that you can comprehend into a list, or you can loop over to view the nodes:
print([p for p in elided_list])
The generator function will return a list of tuples with the first element representing the integer page number of the node, and the second element represeting the text label of the node.
The content that is being paginated (i.e. the actual list of items to be displayed) can be viewed by using the .item_list property of the BetterElidedPaginator class:
# continued from the example above:
item_list = pagination.item_list
print(item_list)
Example
Import the BetterElidedPaginator to the .py file constructing pagination (views.py) in this example
# views.py
from better_elided_pagination.paginators import BetterElidedPaginator
Then use the class inside a view fuction:
# views.py
def homepage(request):
# the items to be paginated - can be a list or queryset
items = [str(x) for x in range(1, 41)]
pagination = BetterElidedPaginator(
request,
items,
3, # items per page
)
return render(request=request,
template_name="home.html",
context={
"pagination_items": pagination.html_list,
"display_items": pagination.item_list
})
In this example, the pagination is in its own template using Tailwind CSS:
# pagination.html
<div class="flex items-center space-x-1 w-full my-2">
{% for item in pagination_items %}
{{ item }}
{% endfor %}
</div>
BetterElidedPaginator - Required Positional Arguments**
- request (Django request object) - The request object made to the view
- object_list (list or queryset) - The list or queryset of objects that is being paginated
- per_page (int) - The number of items per page
BetterElidedPaginator - All Optional Arguments**
- current_page_num [default = 1] - Override the page num typically provided by the request (not recommended)
- pages_on_each_side [default = 2] - The number of pagination nodes that will appear on either side of the middle node when the seleced page is near the middle of the list. A total of five middle nodes will appear by default. If set to "1", three nodes will appear in the middle (the selected node, plus on one each side).
- pages_on_ends [default = 1] - The number of nodes always showing next to the "next" and "prev" buttons.
- next_and_prev_buttons [default = True] - Boolean value for whether the next/prev buttons should be shown on the ends of the pagination element.
- next_button [default = "»"] - String value for the Next button. May use any string such as "Next" or an HTML icon such as Font Awesome.
- prev_button [default = "«"] - String value for the Previous button. May use any string such as "Previous" or an HTML icon such as Font Awesome.
- display_item_range [default = False] - Boolean value for whether the pagination nodes will display item range values instead of page numbers. If the pagination displays five items per page, the first button will have text: "1 - 5" and second button "6-10" instead of "1" and "2".
- css_classes [default = (see below)] - A dictionary which will define the Tailwind CSS classes to use when rendering the pagination elements. The default dictionary may be overriden, but none of the indices should be removed when doing so. The default dictionary is:
css_classes = {
"tw_base": "rounded py-2 px-4 text-center",
"tw_enabled_hover": "hover:bg-blue-100 hover:text-gray-900 hover:shadow",
"tw_enabled_text_color": "text-gray-800",
"tw_disabled": "bg-transparent text-gray-500 cursor-default focus:shadow-none",
"tw_active": "text-white bg-blue-600 shadow-xl",
"outer_div": "",
}
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Hashes for django-better-elided-pagination-1.2.2.tar.gz
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 548d1b7f37c73b7265c095184790210109e4c494e3ba99a68952adb691a23e23 |
|
| MD5 | 214b0e9a51762f8ee6859c5dfb0cd357 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | ad7496297aea0a37a5bfc409c3a1f60ef39214d92b28f0187a6bd8ba05b998f2 |
Hashes for django_better_elided_pagination-1.2.2-py3-none-any.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 166476d2d6ee6d060cfcb464cca24718f4e13d7705a26300fe768beeaab657be |
|
| MD5 | fddf62e032f7d1520951271f83abf42e |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | c481757d3d2ce6979ded0470d272ebee96ec772d17cfb7d5ea2ae816b140c1c1 |











